Understanding Leather Tanning Methods
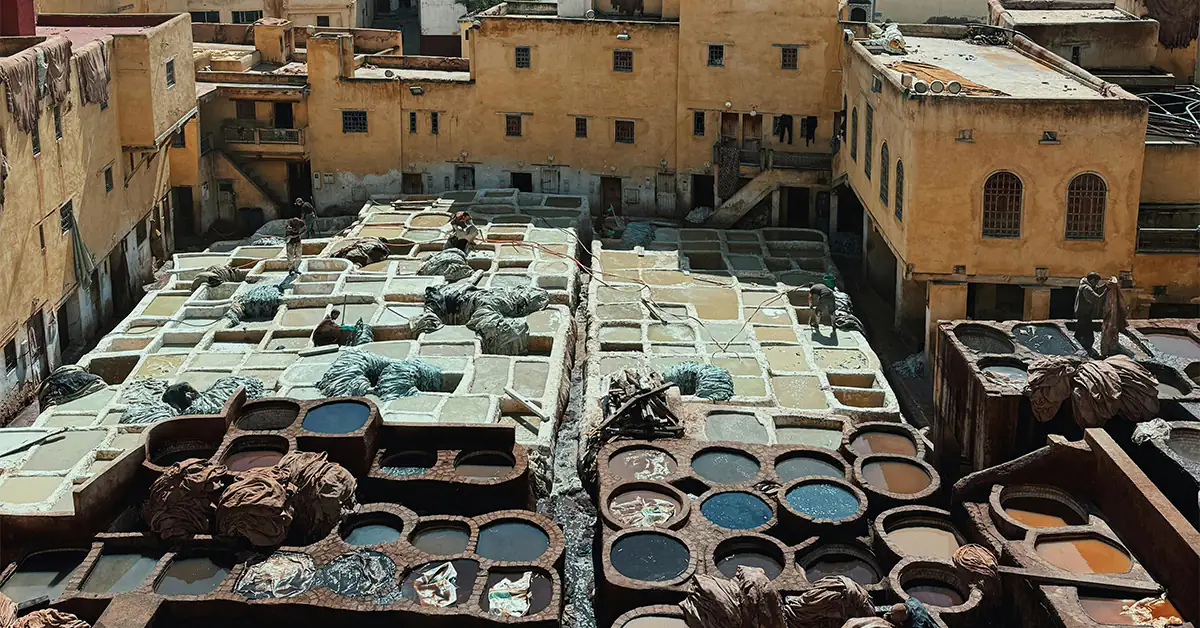

The tanning process transforms raw animal hides into durable, beautiful leather that can last for generations. While most people focus on the finished product, understanding how leather is tanned reveals everything about its quality, characteristics, and environmental impact.
At RADI Leather, we carefully select our tanning methods based on the intended use of each piece, ensuring the highest quality genuine/full-grain leather for every creation. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the three primary tanning methods and help you understand what makes each unique.
What is Leather Tanning?
Before diving into specific methods, it's essential to understand what tanning actually does. Raw animal hides are perishable and will decompose without treatment. Tanning is the chemical process that stabilizes the proteins in the hide, preventing decay and transforming it into leather that's flexible, durable, and long-lasting.
The tanning method used dramatically affects the leather's characteristics, including its color, texture, durability, flexibility, and environmental footprint.
Full Vegetable Tanning: The Traditional Art
What is Full Vegetable Tanning?
Full vegetable tanning, often called veg-tan leather, is the oldest and most traditional method of leather production, dating back thousands of years. This process uses natural tannins extracted from plants, including tree bark (especially oak, chestnut, and mimosa), leaves, and other organic materials.
The Process
The full vegetable tanning process is remarkably time-intensive:
Duration: 30 to 60 days or longer, depending on the thickness and type of hide
Method: Hides are immersed in increasingly concentrated tannin solutions, allowing the natural compounds to slowly penetrate and bind with the collagen fibers in the leather. The process cannot be rushed without compromising quality.
Natural Materials Used:
- Oak bark
- Chestnut tree extracts
- Quebracho wood
- Mimosa bark
- Tara pods
- Myrobalan fruit
Characteristics of Vegetable-Tanned Leather
Appearance: Initially pale tan or light brown, developing rich patina over time
Feel: Firm and slightly stiff when new, becoming supple with use
Smell: Distinctive natural, earthy aroma
Durability: Extremely durable and ages beautifully
Patina Development: Develops the most stunning patina, darkening and gaining character with age and exposure to oils, sunlight, and handling
Water Resistance: Low without additional treatment; absorbs water readily
Moldability: Excellent for tooling, carving, and embossing
Advantages of Full Vegetable Tanning
- Environmentally Friendly: Uses biodegradable, renewable plant materials
- Beautiful Aging: Develops the most attractive patina over time
- Unique Character: Each piece develops its own personality
- Traditional Craftsmanship: Honors centuries-old techniques
- Hypoallergenic: Fewer chemicals mean less risk of skin irritation
- Sustainable: When sourced responsibly, it's the most eco-friendly option
Disadvantages
- Higher Cost: Time-intensive process means premium pricing
- Less Water Resistant: Requires treatment for water protection
- Initial Stiffness: Needs breaking in
- Color Limitations: Naturally produces tan/brown tones; dyeing is possible but less common
- Longer Production Time: Not suitable for fast fashion or mass production
Best Uses
Vegetable-tanned leather is ideal for:
- High-end handbags and briefcases
- Luxury belts and straps
- Artisan wallets
- Saddles and equestrian gear
- Watch bands
- Tooled or carved leather goods
- Items where patina is desired
At RADI Leather, we often choose full vegetable tanning for pieces where we want to showcase the natural beauty of leather and create items that will develop stunning character over decades of use.
Semi-Vegetable Tanning: The Balanced Approach
What is Semi-Vegetable Tanning?
Semi-vegetable tanning, also called combination tanning, is a hybrid method that combines vegetable tanning with chrome tanning techniques. This approach aims to capture the benefits of both methods while minimizing their individual drawbacks.
The Process
Duration: 10 to 30 days, faster than full vegetable tanning but slower than pure chrome tanning
Method: The hide undergoes initial chrome tanning for stability and softness, followed by vegetable tanning to add firmness, improve aging characteristics, and enhance natural aesthetics. The ratio of chrome to vegetable tanning varies based on the desired outcome.
Variations:
- Chrome-retanned with vegetable tannins
- Vegetable-tanned then chrome-retanned
- Simultaneous combination tanning
Characteristics of Semi-Vegetable-Tanned Leather
Appearance: Can range from natural tones to dyed colors, with moderate patina development
Feel: Balanced between firm and supple; more flexible than full veg-tan
Durability: Excellent, combining strengths of both methods
Patina Development: Moderate; ages well but not as dramatically as full vegetable tanning
Water Resistance: Better than full vegetable tanning
Versatility: Can be used for a wider range of applications
Advantages of Semi-Vegetable Tanning
- Balanced Properties: Combines softness with structure
- Faster Production: More efficient than full vegetable tanning
- Cost-Effective: More affordable than pure veg-tan
- Improved Performance: Better water resistance while retaining some natural character
- Versatile: Suitable for more applications
- Still Develops Patina: Ages better than pure chrome-tanned leather
Disadvantages
- Less Distinctive Aging: Won't develop patina as beautifully as full veg-tan
- Environmental Concerns: Contains chrome, though less than pure chrome tanning
- Compromise: Neither fully traditional nor fully modern
- Variable Quality: Results depend heavily on the tanner's skill and ratios used
Best Uses
Semi-vegetable-tanned leather works well for:
- Mid to high-end handbags
- Leather jackets requiring both structure and flexibility
- Quality footwear
- Fashion accessories
- Upholstery where both durability and comfort matter
- Items needing moderate water resistance with natural aesthetics
Chrome Tanning: The Modern Standard
What is Chrome Tanning?
Chrome tanning, invented in 1858, uses chromium salts (primarily chromium sulfate) to tan leather. This method revolutionized the leather industry and now accounts for approximately 80-90% of all leather produced globally.
The Process
Duration: 1 day or less; the fastest tanning method
Method: Hides are treated in rotating drums with chromium salts dissolved in acidic solutions. The chromium compounds bond with the collagen in the hide, stabilizing it quickly and efficiently. After tanning, the leather is dyed, finished, and treated according to its intended use.
Chemical Process: The chromium atoms form stable cross-links with the protein molecules in the hide, creating a molecular structure resistant to heat, water, and bacterial decay.
Characteristics of Chrome-Tanned Leather
Appearance: Can be dyed any color; typically has a uniform, consistent look
Feel: Soft, supple, and flexible from the start
Durability: Excellent resistance to water, heat, and staining
Patina Development: Minimal; maintains its original appearance
Water Resistance: High; naturally more water-resistant
Consistency: Uniform properties throughout the hide
Advantages of Chrome Tanning
- Speed: Dramatically faster production time
- Cost-Effective: Efficiency makes it affordable for mass production
- Softness: Immediately soft and pliable
- Water Resistant: Excellent water and stain resistance
- Color Options: Can be dyed virtually any color
- Consistency: Predictable, uniform results
- Heat Resistant: Better thermal stability than vegetable-tanned leather
- Workability: Easier to cut and sew
Disadvantages
- Environmental Impact: Chromium disposal poses environmental challenges if not properly managed
- No Patina: Doesn't develop character or age dramatically
- Less Natural: Chemical process produces less "authentic" leather feel
- Health Concerns: Poorly processed chrome-tanned leather may contain trace chromium VI (a carcinogen)
- Less Breathable: Generally less breathable than vegetable-tanned leather
- Sustainability Questions: Relies on chemical processing rather than renewable materials
Best Uses
Chrome-tanned leather is ideal for:
- Footwear (especially athletic and outdoor shoes)
- Upholstery and furniture
- Automotive interiors
- Clothing and fashion leather
- Gloves
- Mass-produced accessories
- Any application requiring water resistance and softness
Quality Considerations for Chrome Tanning
Not all chrome-tanned leather is equal. Quality depends on:
- Grade of chrome used
- Proper processing to eliminate harmful chromium VI
- Environmental management of tannery waste
- Quality of the base hide
- Finishing techniques applied
Reputable manufacturers like RADI Leather ensure that when chrome tanning is used, it meets strict environmental and safety standards.
Comparing the Three Methods
Quick Reference Table
| Characteristic | Full Vegetable | Semi-Vegetable | Chrome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tanning Time | 30-60+ days | 10-30 days | 1 day |
| Cost | Highest | Medium | Lowest |
| Environmental Impact | Lowest (if sustainable) | Medium | Highest (if not managed) |
| Patina Development | Excellent | Good | Minimal |
| Water Resistance | Low | Medium | High |
| Initial Softness | Firm | Medium | Very soft |
| Color Options | Limited natural tones | Moderate | Unlimited |
| Aging Characteristics | Beautiful, rich patina | Moderate aging | Minimal change |
| Best For | Luxury, artisan goods | Versatile applications | Mass production, performance |
Which Method is "Best"?
There's no single "best" tanning method. The ideal choice depends on your needs and priorities:
Choose Full Vegetable Tanning When:
- You want leather that ages beautifully
- Environmental impact is a priority
- You appreciate traditional craftsmanship
- The item is meant to last generations
- Natural aesthetics matter most
Choose Semi-Vegetable Tanning When:
- You want balanced properties
- Budget is a consideration but quality matters
- You need moderate water resistance with natural character
- Versatility is important
Choose Chrome Tanning When:
- Immediate softness is required
- Water resistance is critical
- Specific colors are needed
- Production speed matters
- Budget constraints exist
At RADI Leather, we select the tanning method based on each piece's intended purpose, ensuring optimal performance, beauty, and longevity.
RADI Leather's Commitment
At RADI Leather, we're transparent about our materials and methods. Every piece in our collection is crafted from carefully selected genuine/full-grain leather, tanned using methods appropriate to each item's purpose.
We prioritize:
- Quality Over Speed: Choosing tanning methods that enhance longevity
- Transparency: Knowing our supply chain and sharing information with you
- Sustainability: Working with tanneries that meet environmental standards
- Craftsmanship: Honoring traditional techniques while embracing quality innovations
- Beauty: Creating pieces that age gracefully and tell your story
Whether we're creating our award-winning Leather Box Bag or a bespoke piece like the Harry Potter Sorting Hat, we select materials and tanning methods that ensure your RADI creation will be treasured for years to come.
Conclusion
The tanning method used to create leather fundamentally shapes its character, performance, and environmental impact. Full vegetable tanning offers unmatched natural beauty and aging characteristics. Semi-vegetable tanning provides balanced versatility. Chrome tanning delivers immediate softness and practical performance.
No single method is universally superior; each serves different purposes and preferences. By understanding these differences, you can choose leather goods that align with your values, needs, and aesthetic preferences.